GEOAI & Mobility
Unlocking new potentials of geospatial data with state-of-the-art AI solutions
Our AI experts specializing in geospatial data support you in implementing your unique projects in the geospatial domain. With in-depth expertise and cutting-edge technology, we develop tailored solutions to meet your specific requirements.
We divide our expertise into three key areas:
Why Supper & Supper for Your GeoAI Project?
Extensive Industry Knowledge
Our AI experts possess profound knowledge and years of experience in the geospatial domain. We strategically combine this expertise with cutting-edge AI technologies.
Specialization in Geodata
Our team specializes in 2D, 3D, and mobility data. With extensive project experience, we either take on full project responsibility or act as an outsourced workbench.
Strategic Consulting
Drawing on experience from projects with corporations, SMEs, and public institutions, we efficiently address diverse requirements.
Transparent Project Management
We ensure clear communication, regular updates, and maximum transparency—from planning to implementation.
What is GeoAI?
Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI) combines artificial intelligence with geospatial data to analyze spatial relationships and uncover new insights. The focus lies on processing and interpreting geographic information such as 3D models, maps, and satellite data. Through AI methods, complex patterns in mobility and traffic data can be identified, environmental changes modeled, and 2D and 3D data analyzed more efficiently.
With GeoAI, geospatial data is not only visualized but also intelligently interpreted – creating added value in areas such as climate protection, infrastructure management, and mobility. Companies benefit from more efficient processes, improved decision-making, and innovative solutions.


Where is the Added Value of AI in the Geospatial Sector?
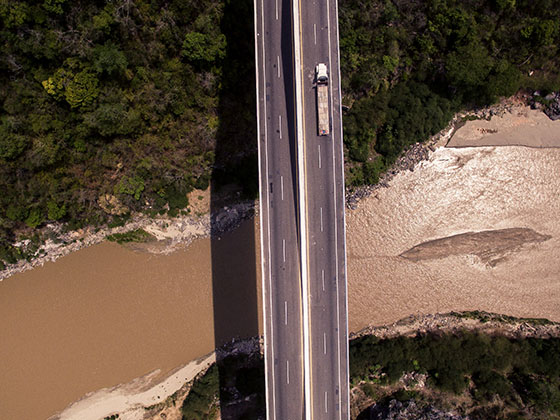
The use of artificial intelligence in the geospatial sector opens up entirely new possibilities for efficiently and accurately utilizing geodata. AI can quickly analyze large volumes of 2D and 3D data, detect complex patterns, and generate predictions that would be unattainable manually. This accelerates decision-making processes and makes them more well-founded.
Particularly in traffic planning, environmental monitoring, and urban development, AI creates significant added value: optimized traffic flows, early risk detection, and sustainable resource utilization. Companies and organizations benefit from automated analyses, improved accuracy, and innovative solutions that help tackle challenges efficiently. With AI in the geospatial domain, data is not only visualized but also transformed into practical, actionable insights—a critical advantage in a data-driven world.
AI on 3D-Data
What Does AI on 3D Data Mean?
AI on 3D data refers to the processing and analysis of complex three-dimensional datasets, such as point clouds, 3D models, and other spatial information. These data provide valuable insights that can be efficiently and accurately utilized through the application of artificial intelligence.
What Do We Do in This Area?
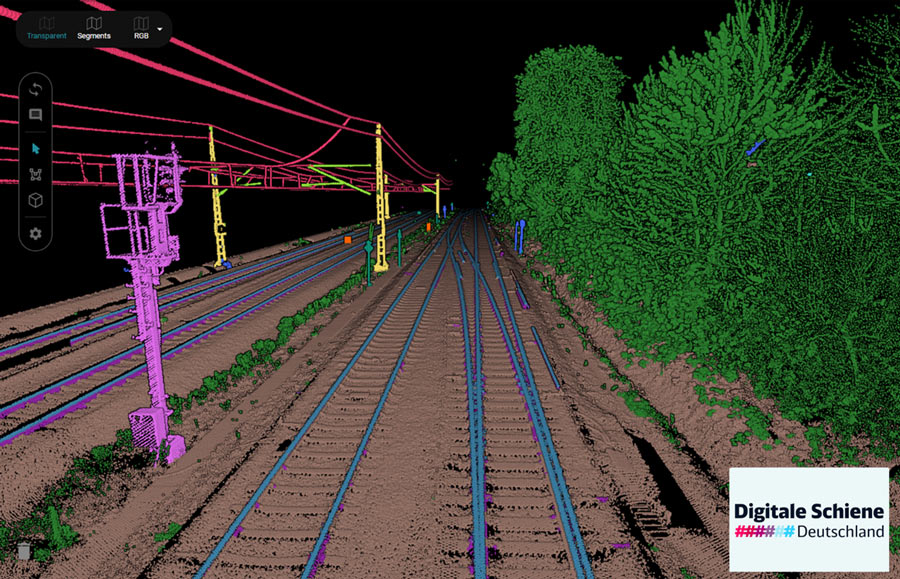
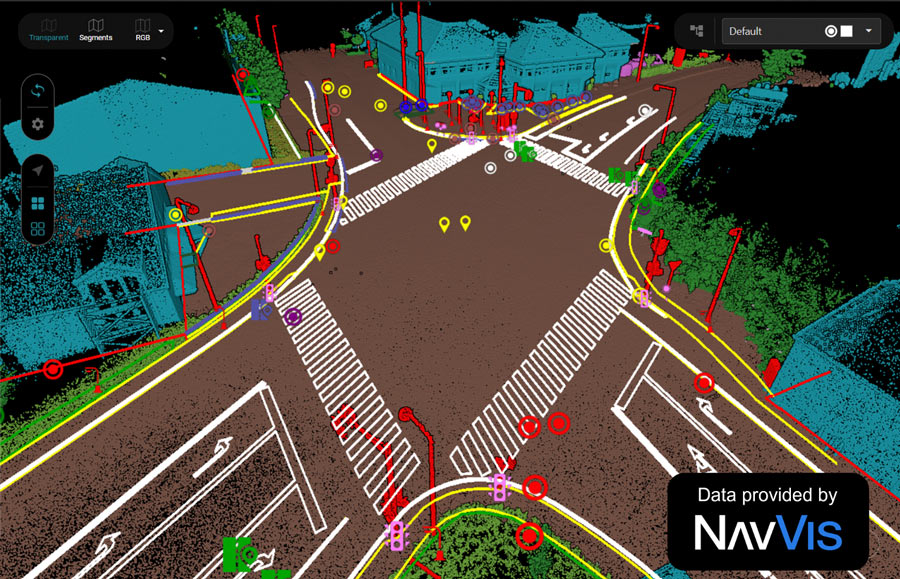
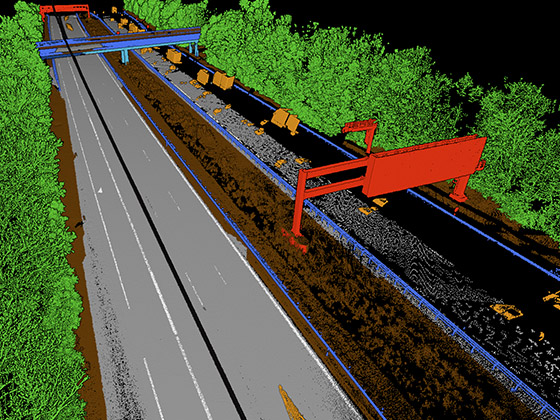
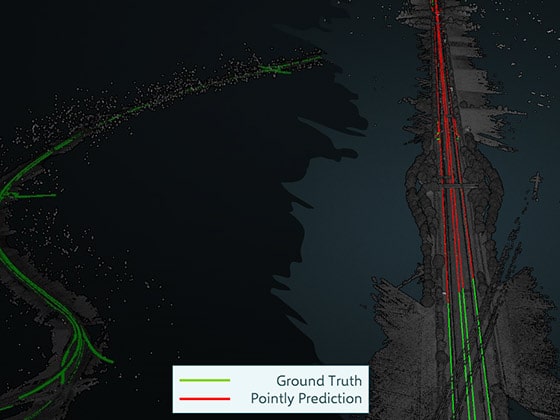
Our team specializes in the analysis of point clouds. Using our platform Pointly.ai, we leverage state-of-the-art AI technologies to classify, structure, and evaluate these complex datasets. This enables fast and scalable processing tailored to diverse industries and applications.
Example Use Cases:
- Urban Planning: Detailed analysis and automatic classification of point clouds to categorize urban structures, optimize designs, and identify potential planning errors early.
- Infrastructure Management: Mapping and analysis of roads, railway infrastructure, and power lines.
- Condition Assessment: Monitoring and maintenance of structures such as bridges or tunnels.
- Agriculture: Leveraging 3D data for precise measurement and classification of agricultural areas.
- Forestry: Classification of tree species and monitoring of forest areas.
- Real Estate: Supporting the creation of high-precision 3D models for construction projects or property valuations.
AI on 2D-Data
What Does AI on 2D Data Mean?
AI on 2D data refers to the processing and analysis of two-dimensional data sources such as satellite images, maps, and geographic raster data. These data are essential for making spatial patterns and relationships visible and enabling data-driven decision-making.
What Do We Do in This Area?
Our focus is on the intelligent evaluation and interpretation of 2D data. Using our AI algorithms, we automate analysis processes, allowing for efficient extraction of relevant information from large datasets. We employ advanced technologies for image and pattern recognition as well as data classification.
Example Use Cases:
- Traffic Management: Identification of traffic flows and bottlenecks in urban areas.
- Urban Planning: Optimization of traffic routes, land use, and traffic sign registries.
- Climate Research: Analysis of satellite data for monitoring environmental changes.
- Agriculture: Detection of cultivated areas and monitoring soil health.
- Disaster Management: Early detection and risk assessment for natural disasters such as floods.
- Infrastructure Management: Precise monitoring and condition assessment of structures like bridges or tunnels.
- Renewable Energy Planning: Optimization of locations for solar farms and wind turbines.

Mobility and geodata
What Does AI on Mobility Data Mean?
AI on mobility data involves the analysis of dynamic data sources such as GPS data, vehicle sensor data, or traffic flow information. These insights enable the identification of mobility patterns, optimization of traffic flows, and development of data-driven solutions for modern mobility concepts.
What Do We Do in This Area?
We process and analyze mobility data from vehicles, sensors, and infrastructure sources to generate actionable insights. Using AI-driven models, we identify bottlenecks, optimize traffic flows, and develop innovative solutions for sustainable and efficient mobility.
Example Use Cases:
- Vehicle Sensor Data: Utilizing real-time data from vehicles for traffic monitoring and management.
- Smart City Integration: Linking mobility data with other urban data sources to enable smarter traffic planning.
- GPS Data Analysis: Detecting movement patterns and optimizing routes.
- Fleet Management: Enhancing efficiency and reducing empty miles in logistics and transport.
- Traffic Flow Optimization: Analyzing data to reduce congestion and improve traffic light coordination.
More Solutions